Exploring Sensory Processing in Autism: Strategies for Support
Understanding individuals who are challenged with sensory processing in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is crucial for providing effective support and improving overall well-being. Sensory processing differences can significantly impact how individuals with autism experience the world around them, influencing their behavior, emotions, and daily functioning. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the intricacies of sensory processing in autism and explore practical strategies to create a supportive environment.
What is Sensory Processing in Autism?
Sensory processing refers to the way the nervous system receives and interprets sensory information from the environment. This includes sensory inputs such as sight, sound, touch, taste, and smell. In autistic individuals, sensory processing differences can manifest in various ways:
- Sensory sensitivities: Some individuals may be hypersensitive to certain sensory stimuli, leading to discomfort or distress in response to everyday sensory experiences such as loud noises, bright lights, or certain textures.
- Sensory seeking behaviors: Others may engage in sensory-seeking behaviors, actively seeking out sensory input to regulate their arousal levels or sensory experiences.
- Sensory processing challenges: Difficulties in processing and integrating sensory information can result in challenges with attention, self-regulation, and behavior.
Creating a Sensory-Friendly Environment
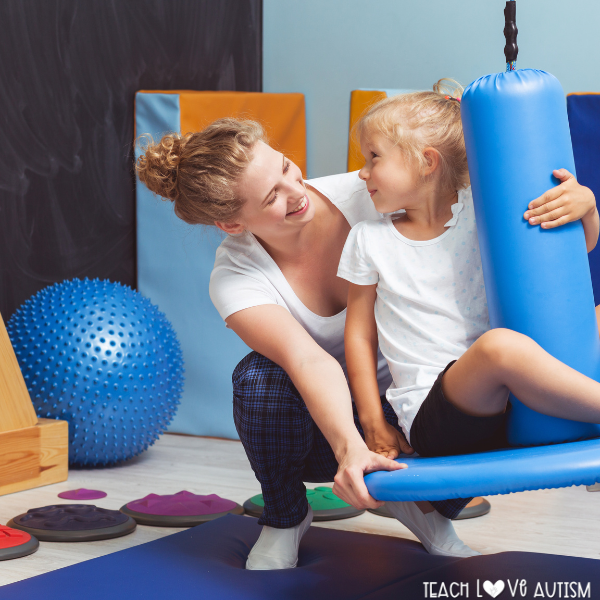
Creating a sensory-friendly environment is vital for supporting autistic individuals in managing sensory challenges. Caregivers can cultivate spaces that promote a sense of safety and comfort by addressing factors that may trigger sensory overload, such as lighting and noise levels. Considering individual sensory preferences and aversions allows for personalized support, empowering autistic individuals to navigate their environment more effectively. Ultimately, a sensory-friendly environment fosters autonomy and emotional regulation, contributing to overall well-being for individuals on the autism spectrum. Here are some tips:
- Minimize sensory triggers: Identify and minimize sensory triggers in the environment, such as loud noises or fluorescent lighting. Use soft lighting, natural materials, and calming colors to create a soothing atmosphere.
- Provide sensory breaks: Offer opportunities for sensory breaks throughout the day to help individuals regulate their sensory experiences. Incorporate sensory-friendly activities such as deep pressure input, swinging, or tactile play.
- Offer choice and control: Allow individuals to have control over their sensory experiences whenever possible. Offer choices regarding sensory input, such as providing options for seating preferences or sensory tools.
Here’s a freebie to help with that! It’s completely editable!
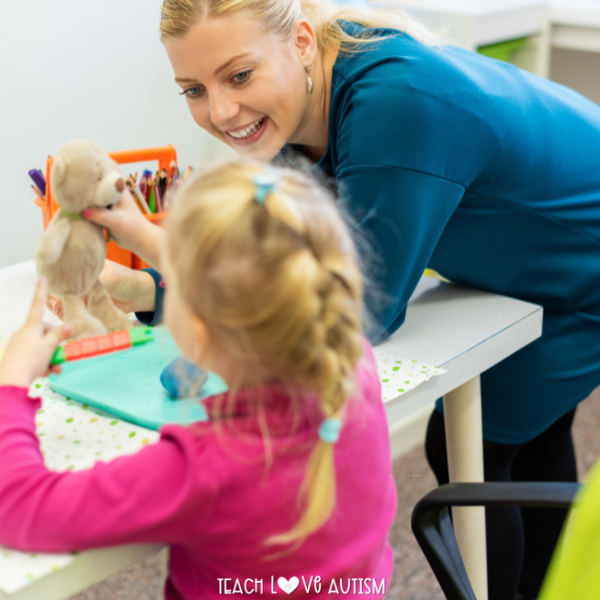
Sensory Tools and Techniques
Utilizing sensory tools and techniques offers invaluable support to autistic individuals in effectively managing sensory challenges. These tools, ranging from weighted blankets to noise-canceling headphones, provide individuals with the means to regulate their sensory experiences and find comfort in their environment. By incorporating such tools into daily routines, caregivers can empower autistic individuals to navigate sensory stimuli with greater ease and confidence. Moreover, these techniques not only enhance sensory integration but also contribute to improved focus, emotional regulation, and overall well-being for individuals on the autism spectrum. Here are some examples:
- Weighted blankets: Weighted blankets provide deep pressure input, promoting relaxation and calming the nervous system.
- Fidget toys: Fidget toys can help individuals regulate sensory input and maintain focus by providing tactile stimulation.
- Noise-canceling headphones: Noise-canceling headphones can reduce auditory sensitivity and provide a quiet sanctuary in noisy environments.
- Visual schedules: Visual schedules and supports can help individuals anticipate and prepare for sensory experiences, reducing anxiety and promoting independence.
Understanding sensory processing in autism is essential for providing tailored support and promoting individual well-being. By creating sensory-friendly environments and utilizing appropriate tools and techniques, we can empower autistic individuals to navigate sensory challenges more effectively and thrive in their daily lives.